Tools for Verifying Accessibility
Verifying Visual Accessibility: Microsoft Office Checkers
Sarah LeMire
If you’re using Microsoft Office products, you can use the built-in accessibility checkers to help you identify potential problem areas.[1] Microsoft’s built-in accessibility checkers work very similarly, though language may differ from one tool to another. For example, while Microsoft Word and PowerPoint refer to alt text as “object description,” Excel uses the term “alt text.” If you are unsure about the issue the accessibility checker has uncovered, you can use the Recommended Actions to gain more information.
One important note: Although the accessibility checkers can be a great resource to double-check yourself, none of these tools is perfect. A manual review of your materials is important to ensure that they are fully accessible.
It is also important to note accessibility is managed differently in desktop-versus-web versions of Microsoft products. For example, the desktop version of PowerPoint offers the ability to adjust the order in which information is presented to assistive technology via the Reading Order Panel, but this same function is done via the Selection panel in PowerPoint 365 on the web. It is important to verify the results of any accessibility tasks you complete to ensure what you intend to do is reflected in the final product.
Word
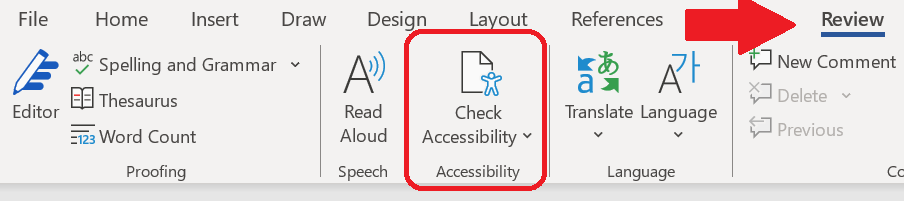
Microsoft Word’s accessibility checker is located under the Review tab. There is an icon labeled “Check Accessibility.” Clicking on this icon will prompt Word to review your document for many accessibility issues, including missing alt text, missing table headings, insufficient contrast, and more.
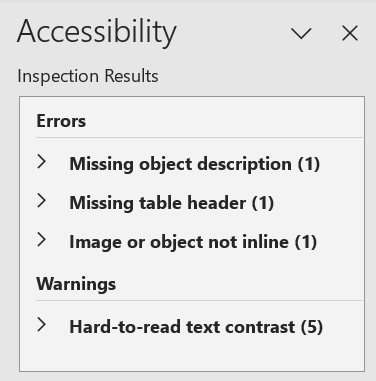
When Word identifies an accessibility issue, it lists it in the Accessibility Inspection Results box that appears in the right-hand toolbar. Microsoft breaks accessibility issues into multiple categories, including errors, warnings, and tips. For example, in the screenshot below, Word identified three errors: missing alt text for an image (“Missing object description”), a table without a header (“Missing table header”), and an image that was embedded within the text rather than between sentences (“Image or object not inline”). In addition, Word is warning that some of the text may not have sufficient contrast “”Hard-to-read text contrast”).
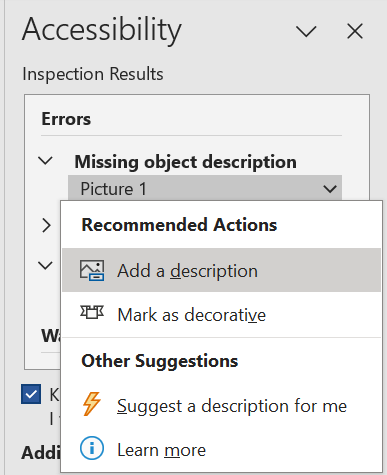
Word will also suggest ways that you can resolve the identified accessibility issues. Clicking on the issue in the Accessibility Inspection Results will bring up the Recommended Actions page. In the example below, Word recommends fixing the image missing alt text by adding the alt text (“Add a description”) or, if the image is merely decorative and does not convey information to the reader, to mark the image as decorative instead.
PowerPoint
Similar to Microsoft Word, PowerPoint contains a built-in accessibility checker that reviews slides for alt text, color contrast, and other common accessibility concerns. The PowerPoint accessibility checker can be found under the Review tab.

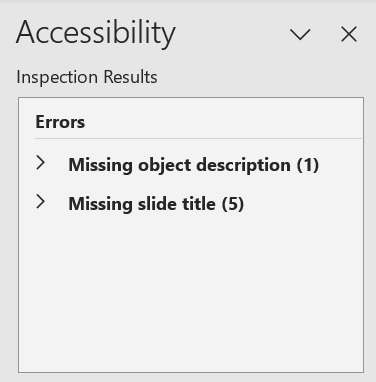
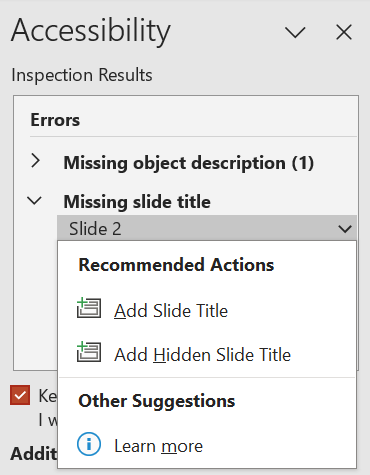
The Check Accessibility feature in PowerPoint checks for many of the same issues as Microsoft Word, but also checks for some slide-specific issues such as missing or duplicated slide headers (Missing slide title). These issues will be reported in the Accessibility Inspection Results in the right-hand toolbar.
To correct the identified accessibility issues, click on the item in the Accessibility Inspection Results pane. When you select a specific item, PowerPoint will recommend how to fix the issue. In this example, PowerPoint suggests either adding a heading to the slide or, if there are design reasons for not using a heading, adding a hidden heading that will be available only to those using a screen reader.
Excel
Microsoft Excel’s accessibility checker works just like that of Word and PowerPoint. The “Check Accessibility” icon can be found under the Review tab.
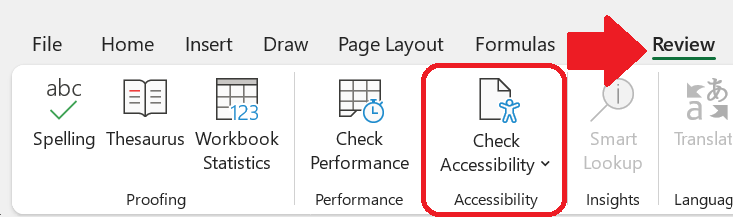
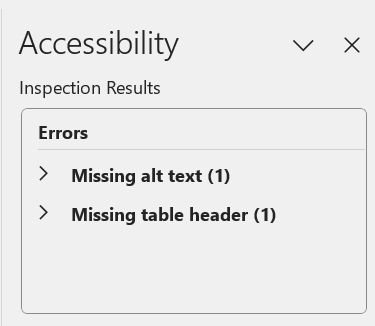
Microsoft Excel checks for many of the same accessibility issues as Word and PowerPoint. For example, it will check to make sure that tables have a defined header and that images such as Excel-created charts have alt text. These issues will be reported in the Accessibility Inspection Results in the right-hand toolbar.
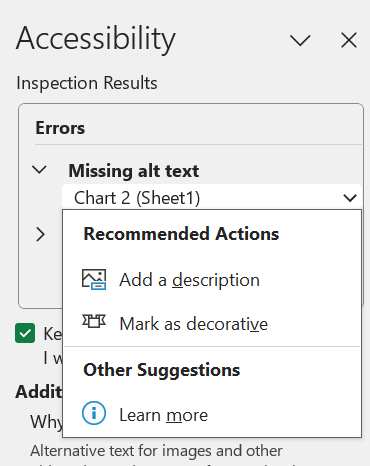
Like the accessibility checker in Word and PowerPoint, the Excel accessibility checker will suggest strategies for resolving identified issues. For example, in the image below, Excel suggests resolving missing alt text for a pie chart by adding a description.
Media Attributions
- Screenshot of the Check Accessibility feature of Microsoft Word 365 edition, May 29, 2024
- Screenshot of the Accessibility Inspection Results feature of Microsoft Word 365 edition, May 29, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Accessibility Inspection Results Recommended Actions feature of Microsoft Word 365, May 29, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Check Accessibility feature of Microsoft PowerPoint 365 edition, May 29, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Accessibility Inspection Results feature of Microsoft PowerPoint 365 edition, May 29, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Accessibility Inspection Results Recommended Actions feature of Microsoft PowerPoint 365 edition, May 29, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Check Accessibility feature of Microsoft Excel 365 edition, June 5, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Accessibility Inspection Results feature of Microsoft Excel 365 edition, June 5, 2024.
- Screenshot of the Accessibility Inspection Results Recommended Actions feature of Microsoft Excel 365 edition, June 5, 2024.
- Microsoft, "Improve Accessibility with the Accessibility Checker," Microsoft Support, accessed 29 May 2024, https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/improve-accessibility-with-the-accessibility-checker-a16f6de0-2f39-4a2b-8bd8-5ad801426c7f ↵

